B. ENERGY CONSERVATION AND EMISSION REDUCTION

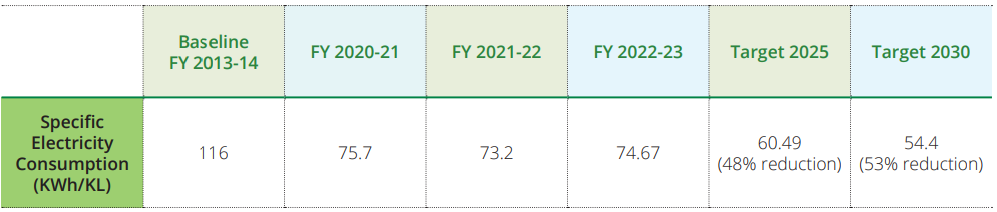
To achieve our target of reducing our Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions, we are working on two enablers: increasing the percentage of renewable electricity to 100% by 2030 and reducing our specific electricity consumption by 53% by 2030 (over 2013-14 baseline).
As part of our overall resource conservation efforts, energy management plays a vital role and is one of the key aspects of
sustainable operations. Our primary focus is on two aspects of energy management:
Our facilities operate with the aim to reduce our energy consumption in the processes which have a direct impact on carbon
emissions.
Energy efficiency
Our efforts to reduce specific and, in turn, absolute energy consumption focus on optimising energy consumption, process
optimisation, installing energy-efficient technologies and conserving/recovering energy through activities such as waste heat
recovery etc. This is enabled by monitoring our performance and conducting energy audits for improvement.
During the year, the total energy consumption at our decorative paint manufacturing units stood at 562,287 GJ and renewable
energy consumption contributed 204,798 GJ.
One of the key metrics that we have been monitoring and concentrating on is Specific Electricity Consumption at our decorative
paint plants. The specific electricity consumption (KWh/KL) is as follows:
In FY 2022-23, there was an increase in electricity consumption at some of our sites due to multiple ongoing expansion projects. In FY 2022-23, total energy consumption on a standalone basis stood at 1,196,127 GJ, out of which 913,261 GJ contributed to direct energy consumption and 282,866 GJ contributed to indirect energy consumption. Out of our total energy consumed, renewable energy consumption contributed 204,798 GJ.
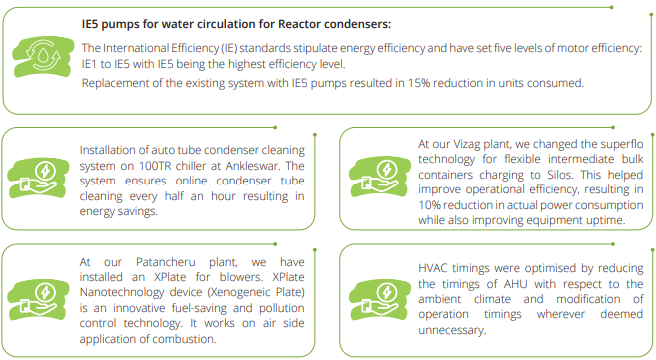
Key energy efficiency initiatives:
Renewable energy usage
We have been making sustained efforts toward transitioning to renewable energy over the last decade through investments in
solar and wind projects. We have an installed capacity of 24.6 MW of solar energy and 24.3 MW capacity of wind energy. The
overall contribution of renewables to electricity consumption stands at 62.2% compared to 61.1% last year.

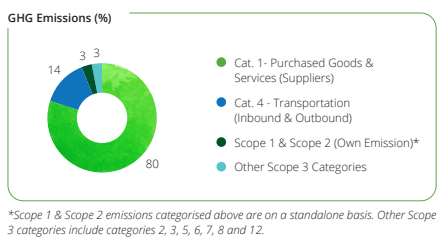
Scope 3 Emissions
During the year, our total scope
3 emissions are estimated to be
33 Lakhs tCO2
e. The category-wise
details have been provided here:

We endeavour to reduce our Scope 3 emissions to transition to low carbon by focussing on:


Supplier Engagement
Engagement with business partners for low carbon transition & responsible sourcing
We recognise the integral role that our suppliers play in achieving our sustainability strategy and our ability to ensure secure supply
to our customers. Nearly 80% of our emissions are contributed by procurement from our suppliers. Hence, our decarbonisation
strategy requires efforts in reducing our value chain emissions and necessitates work with our suppliers.
We are committed to embedding sustainability and resiliency across our value chain through our Sustainable Supply Chain
Framework. This involves adopting a systematic approach to engage with business partners which shall ensure increased
awareness, better disclosure, improved sustainability performance and deep collaboration.
We deploy a well-defined stage-gate process for evaluation and onboarding of prospective suppliers which assesses suppliers
on quality, delivery, price competitiveness and ESG criteria. Suppliers are assessed on legal compliance as well as critical
environmental and social criteria such as comprehensiveness of environmental policy, implementation of the management
system as well as self-declaration on key Human Rights. During the year, 98 suppliers were onboarded based on the above
evaluation and screening criteria.
Our top suppliers representing more than 50% of the raw material procurement by value are certified to be compliant with social
and environmental standards such as SA 8000, ISO 14001, OHSAS 18001 / ISO 45001, EcoVadis (bronze or higher) or any other
relevant labels.

Sustainable Supply Chain Framework:
Our Code of Conduct for Business Partners (“the Code”) sets our expectations from suppliers in terms of their Environmental, Social and Governance performance among other matters. During the year, guided by the Code, we have enhanced and formalised our Sustainable Supply Chain Framework, setting out our approach, expectations, process and promises towards sustainability in the supply chain. We have also established a Responsible Procurement Policy to guide our internal procurement decision-making process in line with the Code of Conduct.

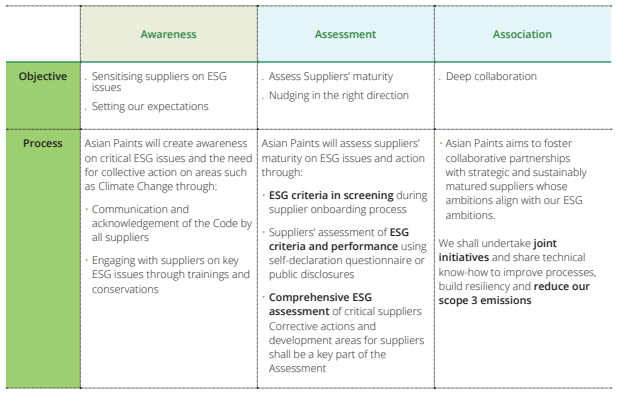
Engagement with suppliers:
The framework enables us to conduct regular supplier reviews to monitor our suppliers’ adherence to the Code. Business partners are expected to comply with requirements, that extend beyond local regulations. Our network of suppliers spans varied geographies, scale of operations and different category of materials. Suitable processes are adopted based on criticality, practicality, and nature of business engagement as well as scale of supplier operations. The engagement comprises 3 levels – Awareness, Assessment and Association and shall aim to shape, assess and improve our suppliers’ sustainability practices and performance as explained in the table below:
Critical Supplier:
Business partners which fall in the top quartile (75%) of value by spend or suppliers having a significant ESG footprint.
Contribution to the transition to low carbon:
The engagement with suppliers is a key enabler for decarbonising our value chain emissions through:

Improvement in emission accounting:
The framework will enable access to primary environment-related value chain data and help us to move from secondary data to primary data in our estimation of emission footprint. The availability of primary data will in turn help in measuring and monitoring the actual impact created by our association with suppliers.
Promoting sustainability:
The framework will help us understand the sustainability performance of our suppliers and help us encourage our suppliers to transition to the use of renewable energy sources.
Association to drive joint initiatives:
The framework shall also help us the identification of business partners with whom we can co-create a path for lower carbon transition. These initiatives could be efficiency improvement in the operations, development and identification of better alternatives and optimisation of products and services.
Key criteria of the framework:
The framework focusses on criteria which are grouped into Environment, Social and Governance themes. The criteria are based upon international sustainability standards such as United Nations Global Compact principles, International Labour Organisation (ILO) conventions, Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) standard, ISO 26000 standard, and CERES principles. Key criteria are listed below:

Outcomes of the assessment:
The assessments will have outcomes at three levels based on the importance of the
criteria:
1. Zero Tolerance:
Some of the criteria are classified as the must-have criteria
where Asian Paints will have zero tolerance.
2. Influence:
This includes positive criteria where supplier will be nudged to
improve ESG performance including monitoring and reporting.
3. Compliance:
This includes criteria against which supplier will be assessed
to improve compliance through corrective actions implementation in a timebound manner.
The assessment will help identify development agenda for improvement in
compliance as well as ESG performance. The assessment will also help in identifying
sustainably matured suppliers and thus pave the way for collaboration for achieving
shared sustainability goals and create an impact.

Supplier performance management:
All Suppliers
We expect all our suppliers to acknowledge our Code of Conduct for Business Partners. As of 30th April 2023, 1,279 existing vendors have acknowledged the policy which includes more than 65% of raw material suppliers by value. • 100% of our new suppliers are screened using Environmental and Social criteria. • Suppliers’ assessment using self-disclosure or publicly available information
Critical Suppliers
• Comprehensive assessment for critical suppliers which may include comprehensive site visits, suppliers certified under international standards such as SEDEX or EcoVadis will be exempted depending on the performance and self-disclosure. We intend to assess 20% of the total critical suppliers in FY 2023-24.
Climate Change Adaptation
In line with the TCFD recommendations, we carried out climate risk assessment
covering both Physical and Transitional risks.
Asian Paints assesses risk factors that may materially and adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition. In line with the TCFD recommendations, we carried out a climate risk assessment covering both Physical and Transitional risks. The assessment helped us improve our understanding of the physical and transition risks we are exposed to, and while the exposure is minimal, it also helped us strengthen resilience measures as part of our adaptation strategy. The outcomes of the assessment are now integrated under our Risk Management framework.
Physical Risk analysis
As part of our physical risk assessment approach, we focussed on analysing acute
risks arising from extreme weather events and chronic risks resulting from longterm changes in climate patterns for our all-eight-paint manufacturing locations
in India. The risks were analysed over the short-term (2030) and long-term (2050),
using IPCC Representative Concentration Pathways – RCP 4.5 (moderate climate
change scenario) & RCP 8.5 (high climate change scenario).
To prioritise the risks, a composite rating was calculated based on the likelihood and
impact of the risks considering RCP 4.5 as probable scenario and short-term (2030)
time horizon to facilitate effective decision-making. Along with scenario analysis
findings, historical events and the probable impact of the risks were also considered
for likelihood and impact scores.
Summary of physical risk and resilience measures:
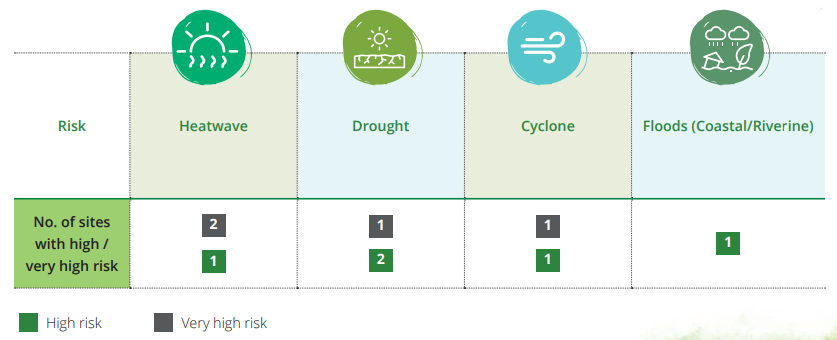
Resilience measures are already part of the design considerations for climate events like cyclones, floods depending on
geographical regions. Similarly, for water risk, our approach already encompasses reduction of non-process water consumption
as well as increasing grey water utilisation across our plants. As per Central Ground Water Board’s classification, none of our sides
are located in Water-stressed area. For other physical risks, resilience measures have been identified and will be implemented
to mitigate the risks envisaged. Details of the risks and the resiliency measures are described in the annexure on Outcomes of
Climate Risk Assessment.
Transition Risk analysis
Transitioning to a lower-carbon economy may entail policy & legal, technology, and market changes. These changes offer both risk and opportunities to the organisation. To analyse potential transition risks for the company, we conducted a comprehensive assessment aligned with the International Energy Agency’s scenarios (IEA SDS) and India’s Net Zero commitments, current and anticipated policies. The transition risks & opportunities identified as part of the assessment as well as the resilience measures are described in the annexure on Outcomes of Climate Risk Assessment.
Risk Management
At Asian Paints, we have a robust and resilient risk management framework as per ISO 31000, which is guided by Risk Management Committee of the Board. The Risk Management Committee closely reviews climate-related risks and mitigation efforts. During the year, we undertook the climate risk assessment as per TCFD recommendations. The physical and transition risks identified through climate risk assessment have been integrated with our Risk Management framework for effective management of these risks. We identified the physical risks using multiple tools primarily through the Aqueduct tool developed by World Resources Institute (WRI), and the World Bank data, India Meteorological Department (IMD) and Central Ground Water Board (CGWB). A composite risk rating was developed for prioritising the risk based on likelihood and impact. We analysed transition-related risks and opportunities through sectoral analysis, International Energy Agency’s scenarios, India’s NDC, analysis of policy & regulatory developments, boundary spanning, and interactions with our Senior Management. An overview of the outcomes of the risk assessment exercise is provided in the annexure to this report. Our efforts towards managing and mitigating our climate-related risks are centred on our approach towards reducing our Scope 1 and Scope 2 GHG emissions, reducing our value-chain emissions, while building resiliency measures in our operations. The details of resilience measures to physical risks have been described in the strategy section. The details around our approach towards managing other climate-related risks and achievements therein can be referred in the Product Stewardship and Environment sections, with key highlights being.

Climate-related Metrics and Targets
At Asian Paints, we assess climate-related risks and opportunities using following metrics: